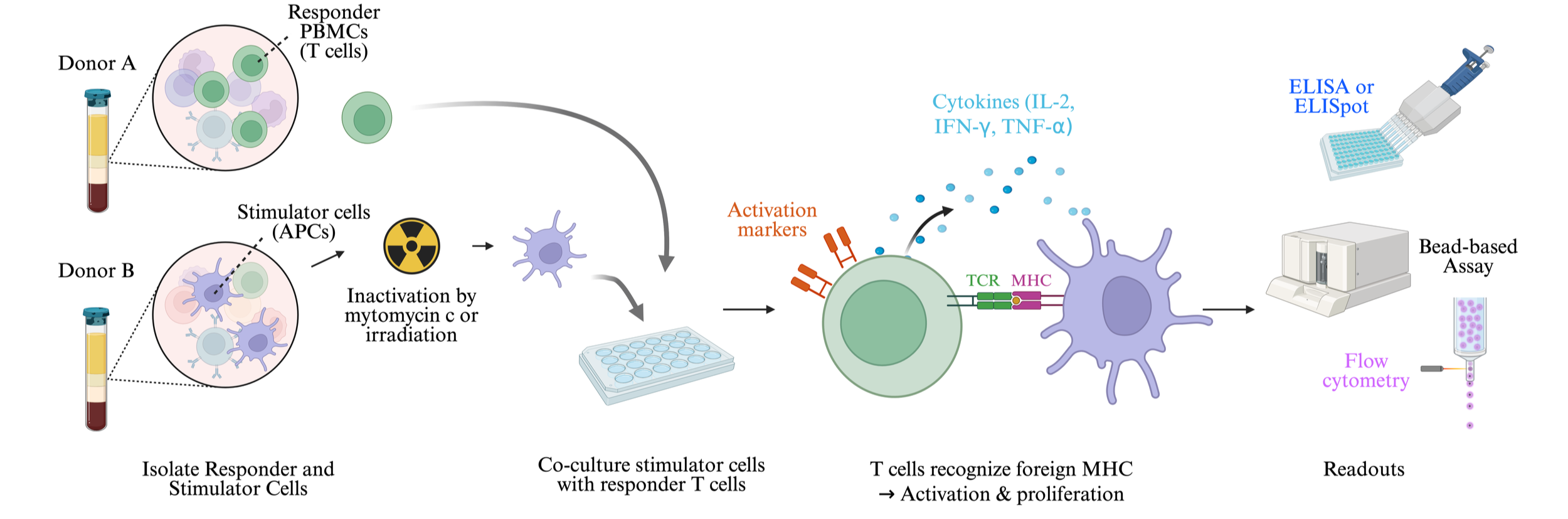
The MLR Assay is a functional in vitro assay used to evaluate T-cell alloreactivity by measuring the proliferation of responder T-cells upon exposure to allogeneic antigen-presenting cells. This assay is widely employed in transplantation immunology, immune tolerance studies, and immunotherapeutic development to assess the strength of alloimmune responses. Allogeneic stimulator cells (PBMC, DC, etc.) are co-cultured with responder T-cells, resulting in T-cell activation and proliferation.
Mixed Lymphocyte Reaction (MLR) Assay
Principle of MLR Assay
Responder T-cells recognize alloantigens presented by stimulator antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
Stimulator cells express foreign MHC molecules, which act as alloantigens.
Responder T cells become activated upon recognition of foreign MHC molecules.
Activated T cells proliferate and upregulate activation markers (e.g., CD69, CD25).
T cell response is measured using various readouts:
Proliferation assays
Cytokine secretion (IFN-γ, IL-2) using ELISA or multiplex assays.
Flow cytometry for activation marker expression and proliferation assessment.
Readouts
T cell activation markers:
CD69 and CD25 expression measured by flow cytometry.
Cytokine secretion assays:
ELISA or multiplex assays to measure IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α levels.
Add-On Services
Evaluation of cytokine release, proteomics, and transcriptomics.
Key Components of MLR Assay
A. Responder Cells (T Cells):
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) or purified CD4⁺/CD8⁺ T cells.
Recognize foreign MHC molecules and initiate an immune response.
B. Stimulator Cells (Antigen-Presenting Cells, APCs):
Can be PBMCs, dendritic cells, or B cells from a genetically different donor.
Provide alloantigens (foreign MHC molecules) for T cell activation.
In one-way MLR, stimulator cells are inactivated (irradiated or mitomycin C-treated)
to prevent their proliferation.