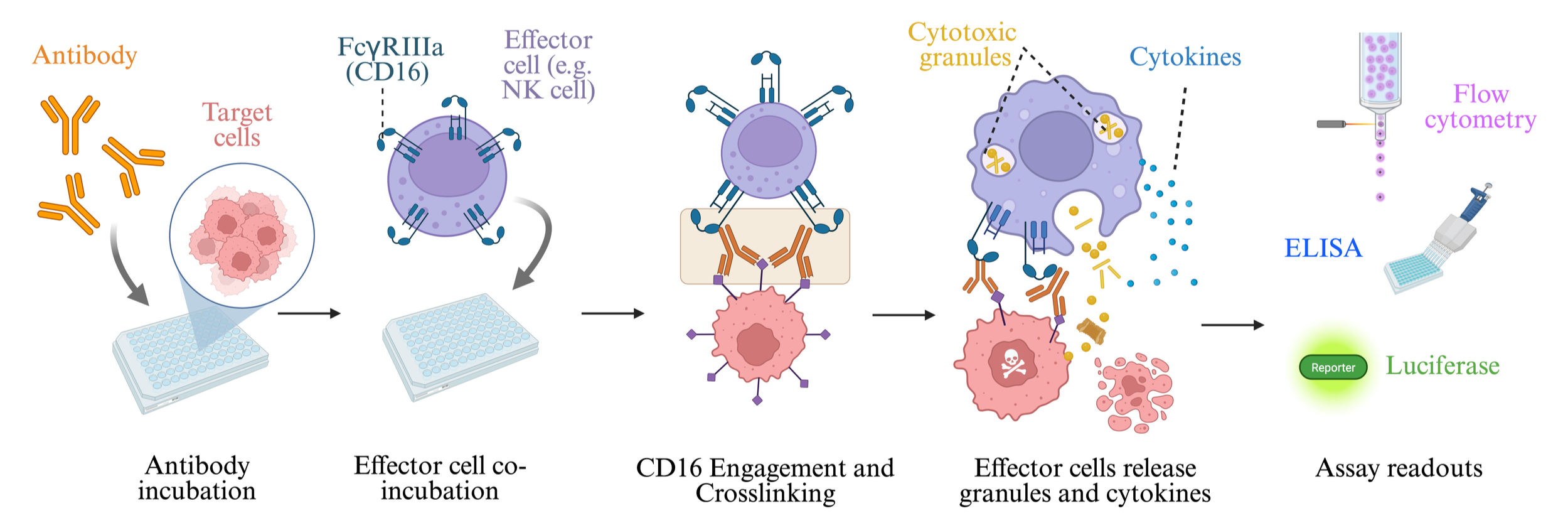
ADCC assays are designed to evaluate the ability of therapeutic antibodies to mediate immune effector cell killing of target cells via Fc receptor (FcγR) engagement. Cancer cells expressing the target antigen are co-cultured with NK cells and the monoclonal antibody, resulting in target cell destruction.
Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC) Assay
Principle of ADCC Assay
Target cells (e.g., cancer cells or virus-infected cells) express the antigen of interest.
Therapeutic antibody (IgG1) binds to the antigen on the target cell surface.
Effector cells (e.g., natural killer (NK) cells, monocytes, or engineered cell lines) recognize the antibody via CD16 (FcγRIII) on their surface.
Effector cells release cytotoxic molecules (e.g., perforin, granzymes, TNF-α), leading to target cell lysis.
Cytotoxicity is measured using various readouts (e.g., LDH release, luciferase, or flow cytometry).
Readouts
Tumor cell destruction (apoptosis) by flow cytometry, NK cell response by cytokine secretion (IFNγ release) and luciferase-based reporter expression.
Add-On Services
Evaluation of cytokine release, NK cell cytotoxic factors (perforin/granzymes), proteomics, and transcriptomics.
Key Components of ADCC Assay
A. Target Cells
Should express the specific antigen recognized by the monoclonal antibody (tumor cells or virus-infected cells).
B. Effector Cells
NK cells (primary mediators of ADCC).
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) (contain NK cells & monocytes).
Jurkat NFAT-Luc reporter cells expressing CD16 (engineered cell lines for FcγR activation).
C. Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies (e.g., IgG1 with strong FcγR binding).
Engineered antibodies with enhanced Fc-mediated effector functions.